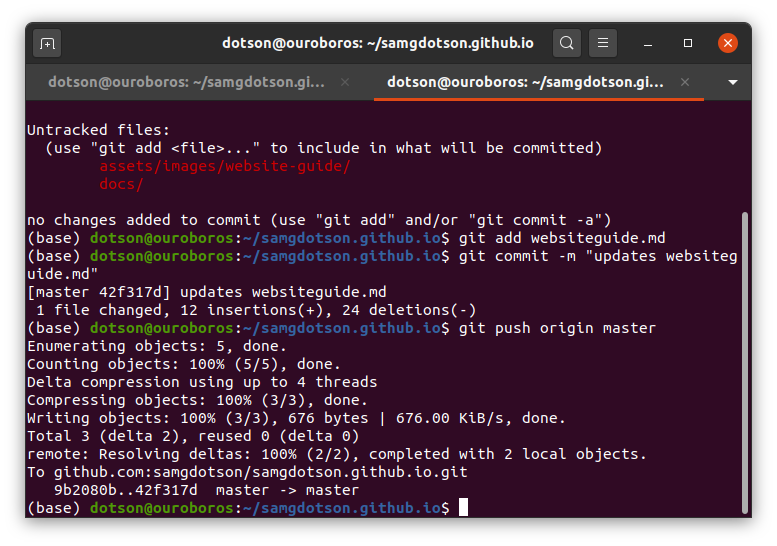
If you want to check your work before publishing to your live website, keep reading!
Step 0: Install Git on Your Computer
In order to do this you have to install Git. Git is a local version control software that couples with GitHub for cloud storage (among other benefits).
Follow these instructions to install Git.
Step 1: Install Jekyll and its Dependencies
GitHub pages is based on Jekyll which is built in the Ruby programming language. You don’t have to know Ruby to use Jekyll.
Follow this guide on Jekyll installation.
Step 2 Adding a Gemfile
In order to build your website locally, you’ll have to create a Gemfile and
put it in your top level directory.
- In your website repository simply select “Create new file”
- Call it
Gemfile(no extension) - Add the code:
source 'https://rubygems.org'
gem 'jekyll', '3.8.5'
group :jekyll_plugins do
gem 'jekyll-theme-cayman'
end
- Commit your changes once again!
- Note:
jekyll-theme-caymanshould be changed to the theme that you chose.
Step 3: Clone the Repository to Your Local Machine
You have two options
- With SSH-keys
- With an HTTPS link
Note: The advantage of SSH keys is that it establishes a secure connection between your computer and GitHub, so you don’t have to sign in every time you want to commit a change. If you’re new to GitHub, however, you do not need to set up SSH keys.
In either case you will need to do the following:
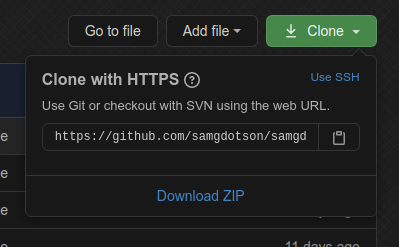
- Copy the text
https://github.com/... - Open Terminal (for Linux/Ubuntu) or Command Prompt (for Windows)
- Enter the following code:
git clone [url-link]
[url-link] is the link you just copied, you can paste it into terminal by
Linux/Mac: shift+ctrl+v
Windows: ctrl+v
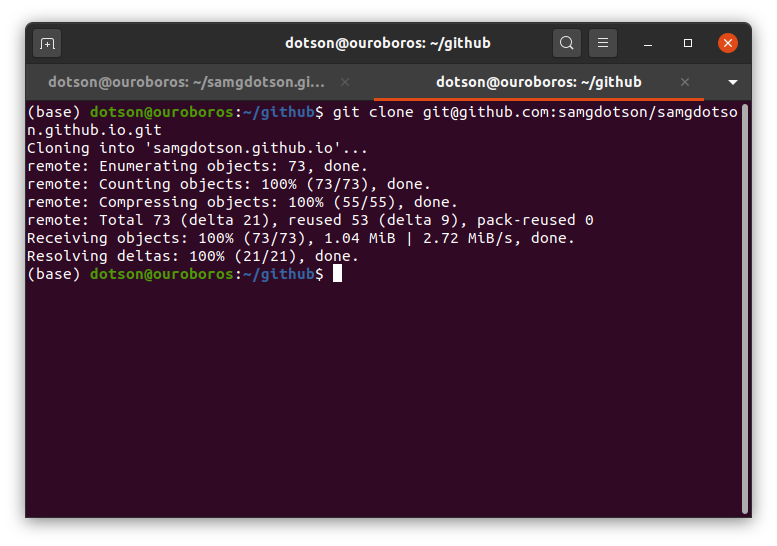
Step 4: Build your website locally
Open terminal or command prompt and navigate to your repository with
cd [username].github.io
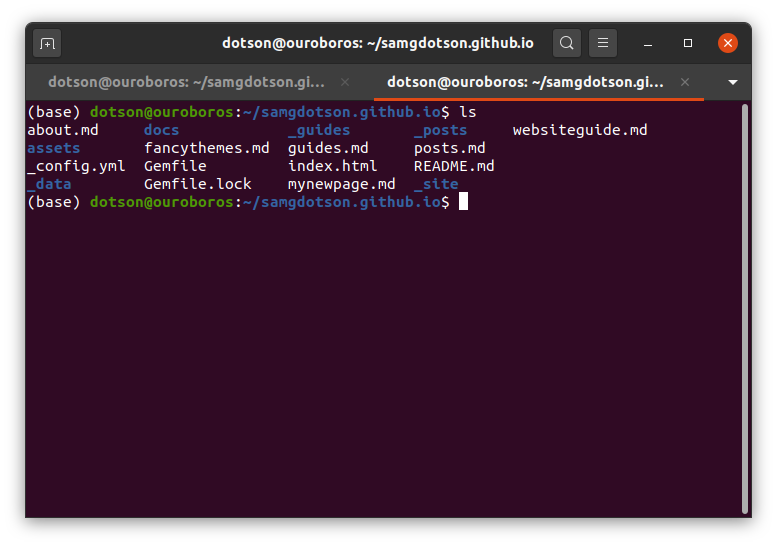
Check if your Gemfile is in the repo by doing
Linux/Mac: ls
Windows: dir
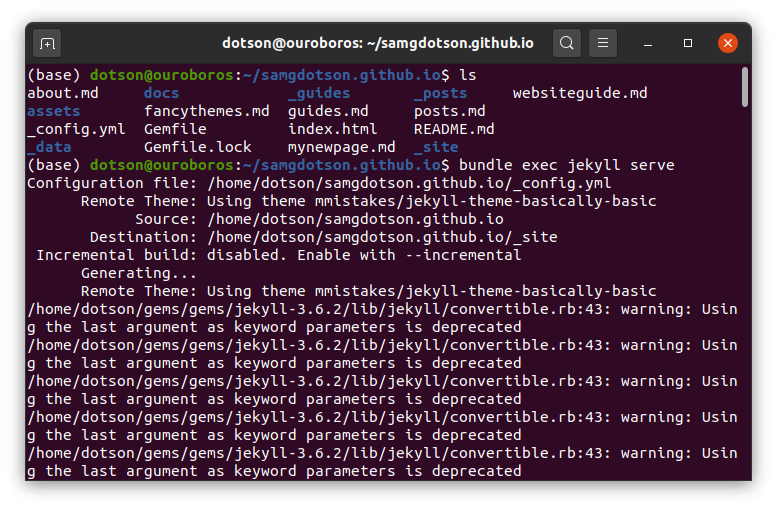
Finally, build your website locally with
bundle exec jekyll serve
you may have to run bundle install. Jekyll should tell you what to do
in the error message.
Step 5: Open Your Website in a Browser
Open an internet browser and type localhost:4000 in the address bar.
Voila! You can now see your website as it exists in your repo before you commit changes to it!
Step 6: Making Changes
Making changes to your website locally is powerful. However, to do so you need a text editor (MS Word is not a text editor).
Atom is my favorite, but any will do (Notepad, Notepad++, SublimeText, …).
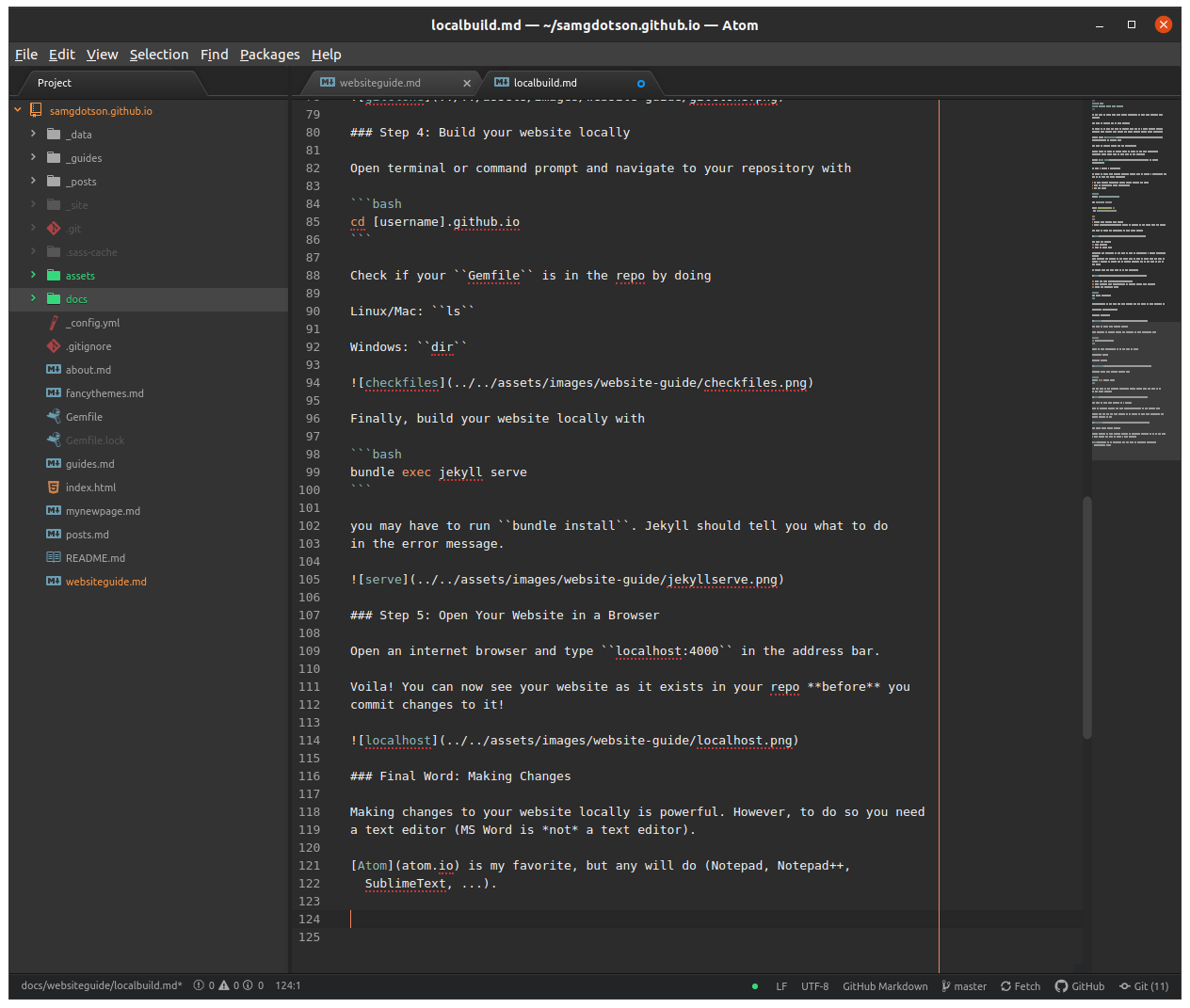 A screenshot from my text editor, Atom
A screenshot from my text editor, Atom
Save your changes and refresh the localhost:4000 page to see them.
Step 7: Publishing Changes
You’re happy with the changes you’ve made to mynewpage.md and you want
to publish them to your live website.
Open your Terminal/Command Prompt again and do the following,
git status
git add mynewpage.md
git commit -m "Adding mynewpage.md"
git push origin [branch]